Foundations of Electronics
“Electronics is the silent symphony that powers our modern world — and it all begins with a few humble components.”
Our journey begins with a deep understanding of the basic components of electronics. Just as alphabets make words, these components form the building blocks of all electronic systems.

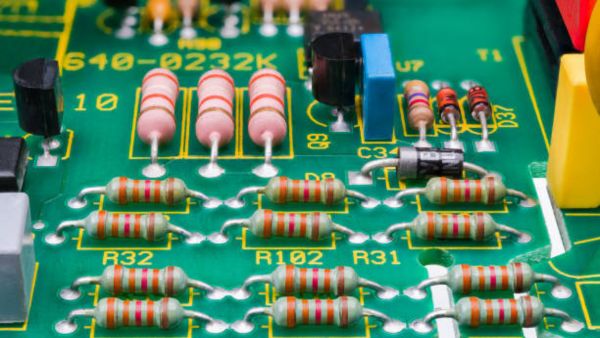
Resistors
A resistor is used to control the flow of electric current in a circuit. It provides resistance, just as a narrow pipe slows down water flow. Applications - Controlling brightness of LEDs, Voltage division, Protecting sensitive components

Capacitors
The Mini Energy Tank. A capacitor stores electrical energy and releases it when needed. It charges and discharges, helping smooth out voltage fluctuations. Applications - Power supplies, Signal filtering in audio systems, Camera flashes.

Diode
The One-Way Guardian. A diode allows current to flow in only one direction, blocking reverse flow. (i) Types - LED (Light Emitting Diode) – glows when powered. (ii) Zener Diode – allows reverse flow after a certain voltage. Applications - Current rectification, Voltage regulation, LED indicators.

Inductors
The Magnetic Muscle. An inductor stores energy in the form of a magnetic field when current passes through it. It resists changes in current. Applications -Transformers, Radio tuning circuits, Energy storage in buck converters.

Switchs
The Power Decider. A switch is used to manually or automatically open or close an electrical circuit. Applications - Home automation, Circuit debugging & Robotics control panels.

Potentiometer
A potentiometer allows for adjustable resistance in a circuit. Applications - Volume control, Sensor calibration & Game joysticks.
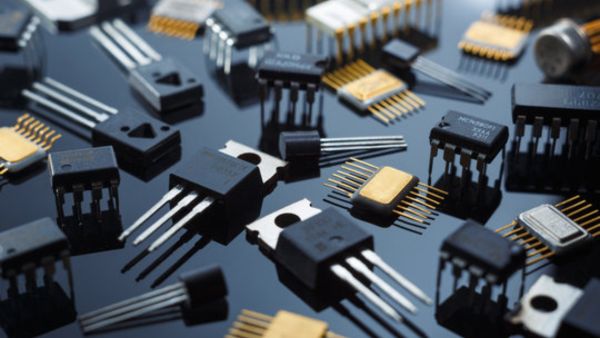
Transistors
The Intelligent Switch. A transistor acts as a switch or amplifier. It controls a large current using a small input signal. Types - NPN / PNP & MOSFET. Applications - Amplifiers in audio systems, Logic gates in computers & Microcontrollers and robotics

Battery
The Power Source. A battery is use to maintain the potential difference across circuit & provides the electrical energy required to run a circuit. Applications - Portable electronics, Robotics, Backup power.

Integrated Circuits (ICs)
Brains in a Black Box. An IC combines many components (transistors, resistors, diodes) into a tiny chip. Applications - Microcontrollers (Arduino, 555 Timer IC), Smartphones & Embedded systems

Connectors and Wires
The Lifelines. Connecting wires link each component, ensuring smooth communication between sensors, actuators, processors, and power sources. Applications - Jumper wires in breadboards, Terminal blocks & Communication cables etc.
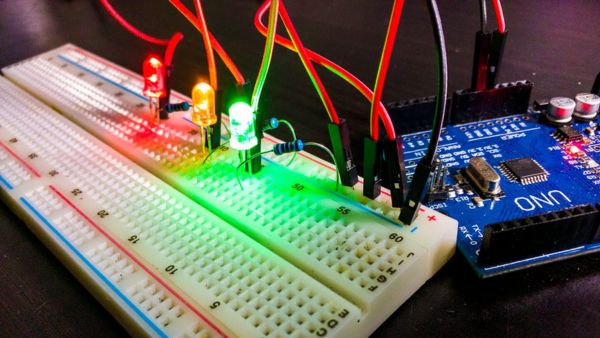
Breadboard
Reusable Platform . A breadboard is used to build and test electronic circuits without soldering. It allows students & engineers to experiment, modify, and troubleshoot circuits easily, making it an essential tool for STEM and robotics education.

Soldering
Powerful join. Soldering is the process of joining electronic components by melting a metal alloy to create a permanent, conductive connection. It ensures reliable performance in circuits, making it vital for robotics, electronics projects, and ATL innovations.
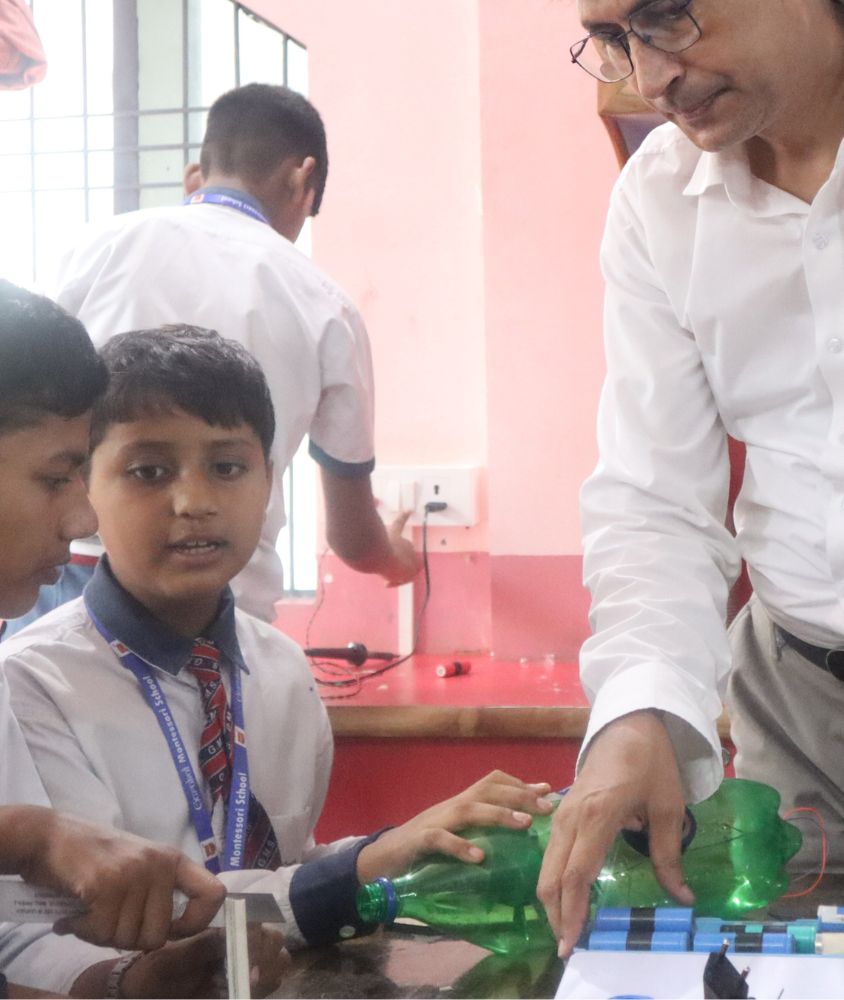
Robotics & AI Faculty
I nurture young minds to design, build, and control the technology of tomorrow.

Er. Faisal Nadeem
A dedicated educator with a strong academic foundation, holding a B.Sc. in Mathematics, Physics, B.Tech, and M.Tech in Electronics Communication. I am also a Cisco Certified Network Associate and Microsoft Certified Professional. Currently, I serve as a A.T.L Faculty at “Gurukul Montessori School (G.M.S)”, one of the finest educational institutions in Allahabad (U.P).







